New Zealand Election System Explained
You just pick the person in your area you think best advances your interests and the political party that best represents your interests.
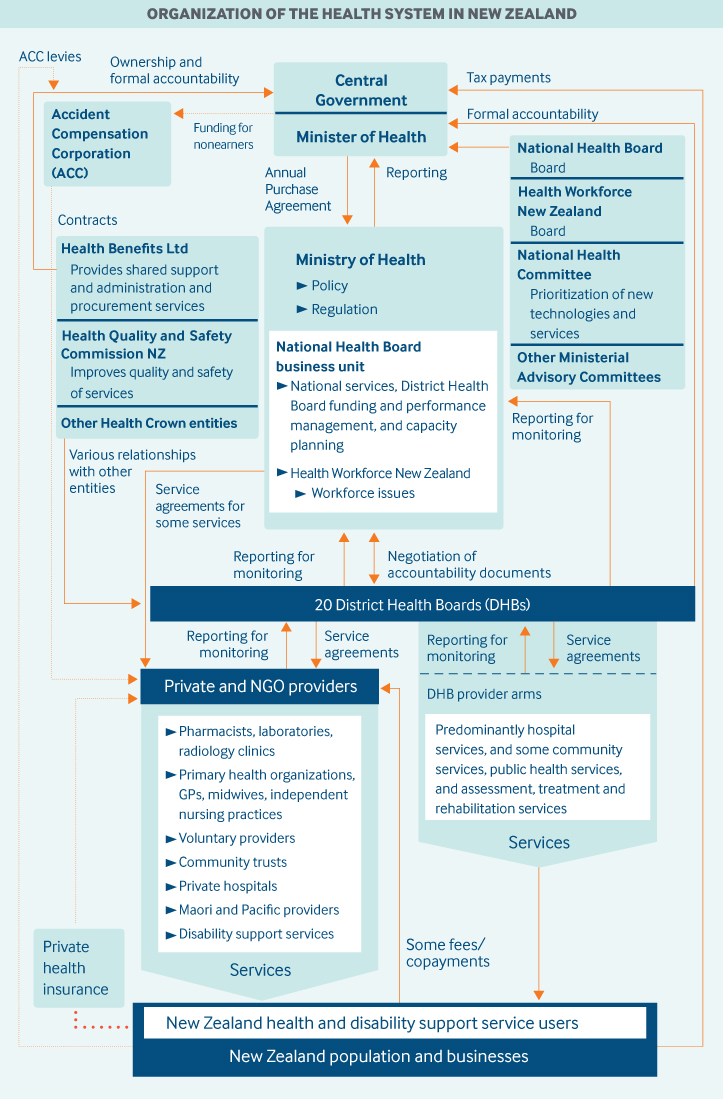
New zealand election system explained. This will also be the first time that a party will be governing alone since new zealand moved to the mmp mixed member proportional representation electoral system in 1996. The 52nd parliament elected in 2017 has 120 seat. Ardern s party has won a majority the biggest victory for the labour party in over 50 years.
The system of government nz is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system of government. Mmp aims to ensure that people will be represented in parliament both by a person in their local area electorate and by a group a political party. Mmp is the voting system we use in new zealand.
It turned out to be one of the closest races in new zealand s history full of twists and turns and endi. In 1993 a general election year in new zealand voters had the chance to vote on a binding national referendum on the voting system. New zealand s government was based on the british model.
New zealanders have two votes one for a local representative and one for a political party. With nearly 50 per cent of the vote the party will get more than the 61 seats required for a parliamentary majority. The government is formed after a democratic election held every 3 years.
How does it work. Mmp aims to ensure that people will be represented in parliament both by a person in their local area electorate and by a group a political. It stands for mixed member proportional.
This means that our head of state is a sovereign currently queen elizabeth ii. We use mmp to choose who represents us in parliament. Most electorates had only one member of parliament mp but some had more than one.