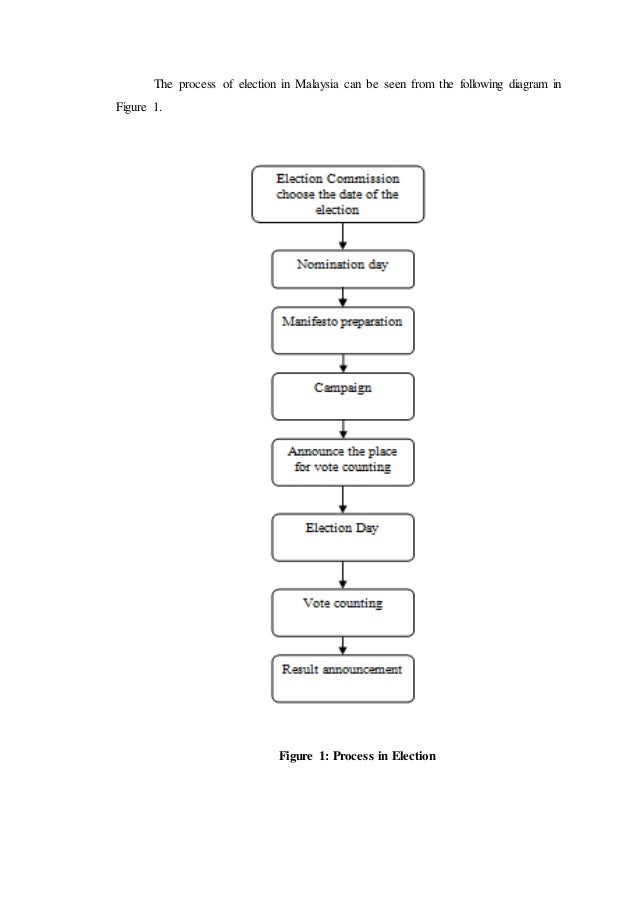
Election System Of Malaysia

Elections in malaysia exists at two levels.
Election system of malaysia. Compared to western and developed countries their political parties are based on pragmatic ideological orientation although they still maintain the major ideologies liberal democrat conservative socialist feminist to distinguished among them. Under the constitution the primary function of the ec is to conduct elections to the dewan rakyat and the state legislative assemblies. The election commission ec runs the election process.
The electorate in each constituency vote for their member of parliament to sit in the lower house of parliament the dewan rakyat. The federal level and the state level. 12 such as the barisan alternatif ba.
Two types of elections. 11 despite the recent setback in the 2008 elections where the ruling coalition lost power in five states in peninsular malaysia. At present elections in malaysia exist at two levels.
Introduction elections are a unique area of public governance being large scale national events. Under fptp constituencies are allocated to component parties on a near permanent basis normally based on ethnic composition of the constituencies and previous contestation history. Federal level and state level.
The ultimate flaw of malaysia s party system lies in permanent coalitions a la bn which provides no avenue for internal competition and becomes prone to sub competitiveness infighting or both. Federal level elections are those for membership in the dewan rakyat the lower house of parliament while state level elections are for membership in the various state legislative assemblies. The heads of executive branch at both the federal and state levels the prime m.
The winner does not have to win. The country is geographically divided into constituencies. 10 the barisan nasional bn comprising mainly the united malays national organisation umno the malayan chinese association mca and the malayan indian congress mic.